BitWise Source Separation
- Paper accepted by International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 2018 (arXiv). (2018/2)
- Presented as a poster at 2017 NIPS Workshop on Machine Learning for Audio. (2017/12)
- For any question please contact lijguo@gmail.com.
Intro
This paper proposes an efficient bitwise solution to the single-channel source separation task. Most dictionary-based source separation algorithms rely on iterative update rules during the run time, which becomes computationally costly especially when we employ an overcomplete dictionary and sparse encoding that tend to give better separation results. To avoid such cost we propose a bitwise scheme on hashed spectra that leads to an efficient posterior probability calculation. For each source, the algorithm uses a partial rank order metric to extract robust features that form a binarized dictionary of hashed spectra. Then, for a mixture spectrum, its hash code is compared with each source’s hashed dictionary in one pass. This simple voting-based dictionary search allows a fast and iteration-free estimation of ratio masking at each bin of a signal spectrogram. We verify that the proposed BitWise Source Separation (BWSS) algorithm produces sensible source separation results for the single-channel speech denoising task. To our knowledge, this is the first dictionary based algorithm for this task that is completely iteration-free in both training and testing.
Demo
For each of ten noises, here we present the denoised speech along with the spectrograms.
Mean SDR by Noise (DB)
| Noise | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Bird | 7.36 | 7.36 |
| Casino | 4.05 | 4.22 |
| Cicade | 13.82 | 14.92 |
| Computer keyboard | 7.39 | 6.85 |
| Eating chips | 7.01 | 7.52 |
| Frogs | 7.72 | 7.88 |
| Jungle | 4.33 | 4.79 |
| Machine guns | 9.80 | 8.78 |
| Motorcycles | 8.06 | 7.07 |
| Ocean | 5.73 | 4.83 |
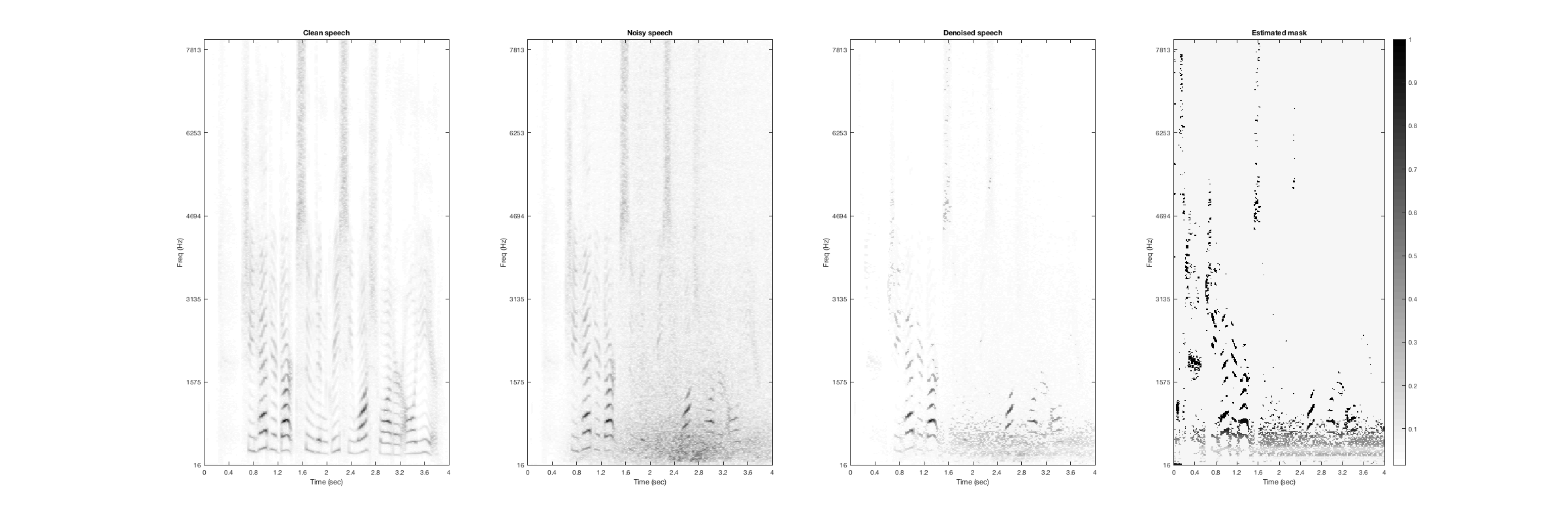
Bird
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 7.2902):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
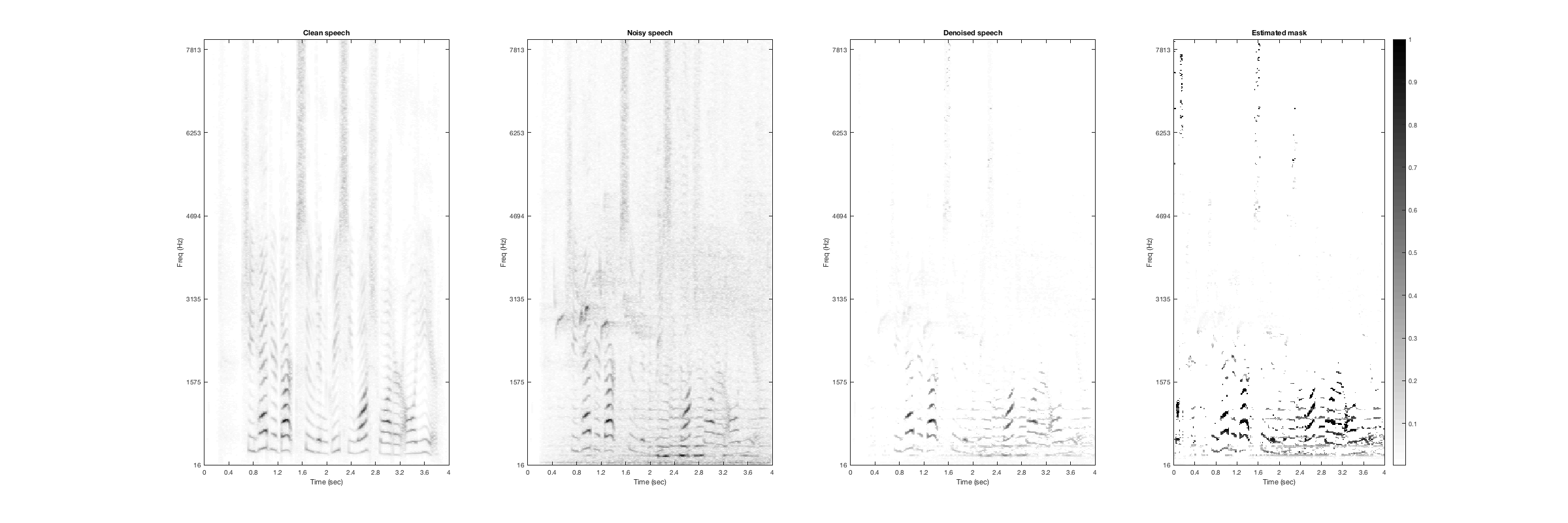
Casino
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 3.632):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
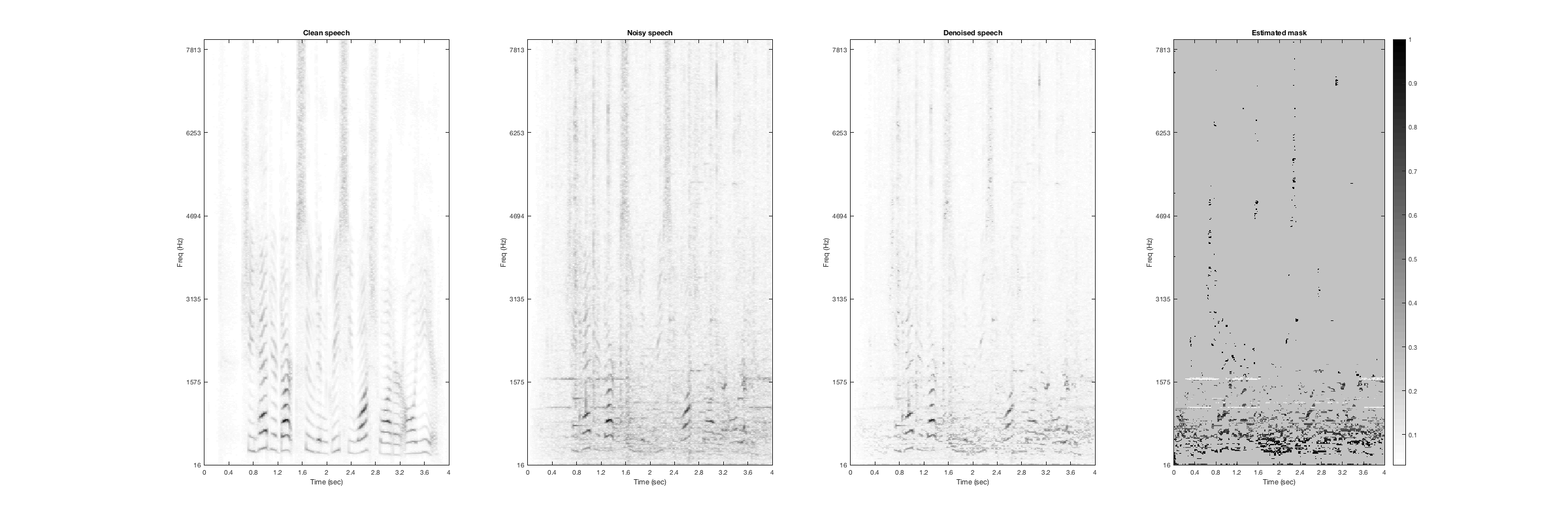
Cicade
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 12.901):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
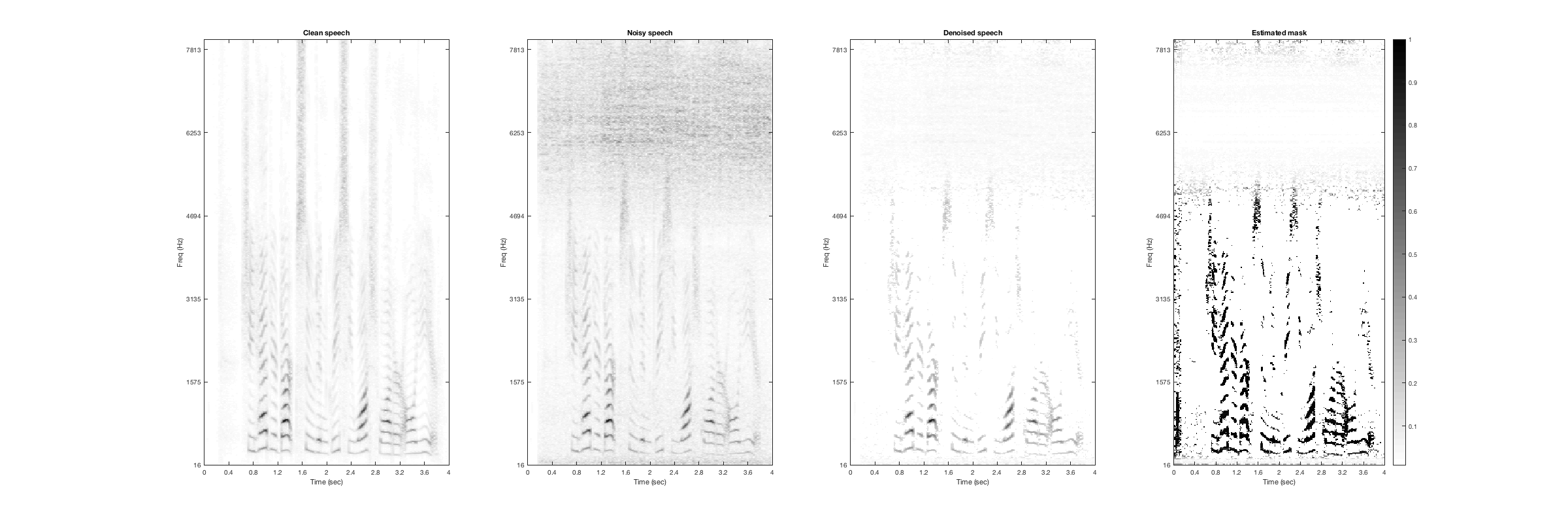
Computer keyboard
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 7.2988):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
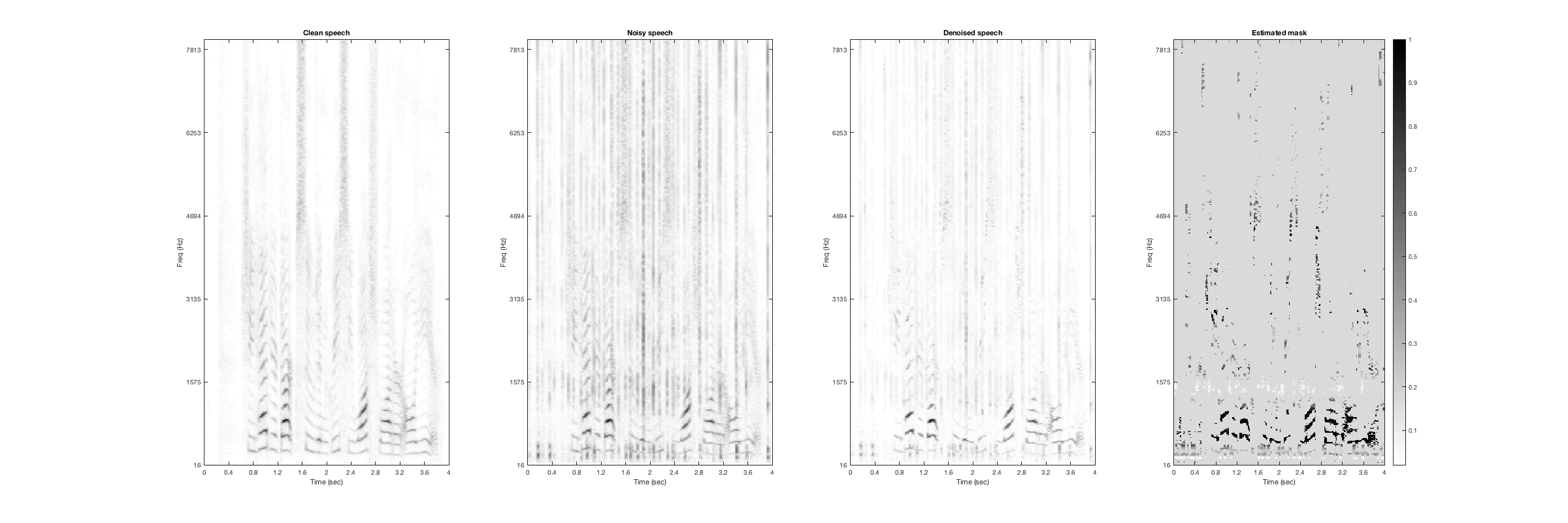
Eating chips
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 7.0808):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
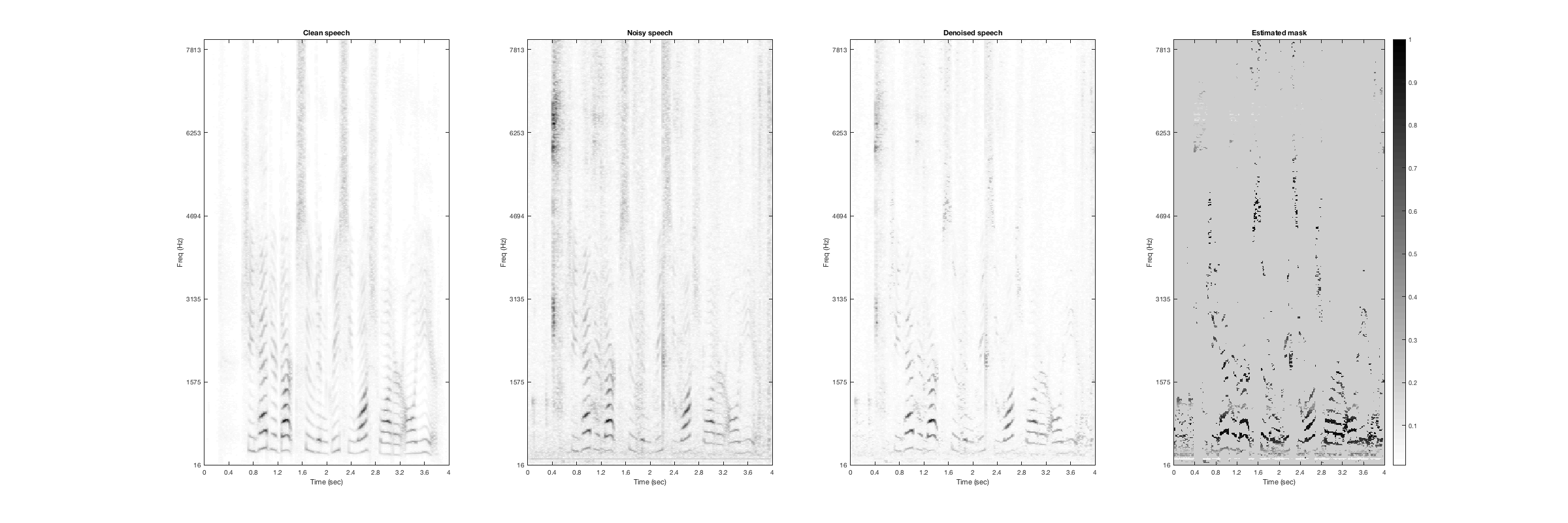
Frog
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 7.1883):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
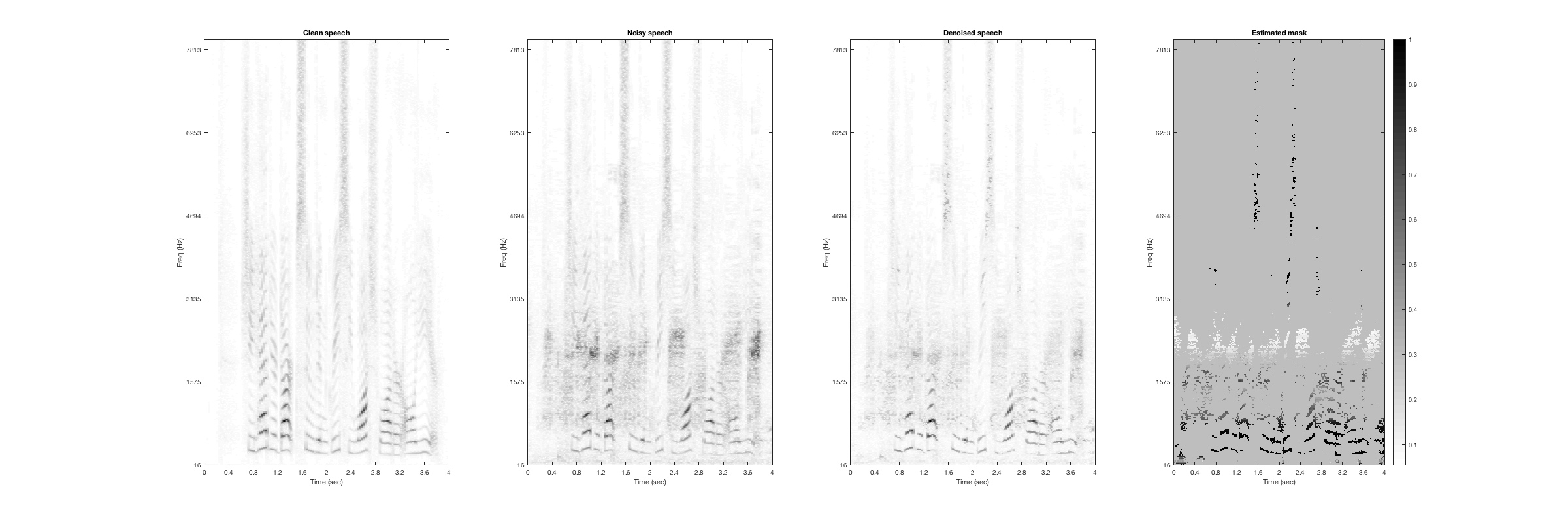
Jungle
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 3.2841):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
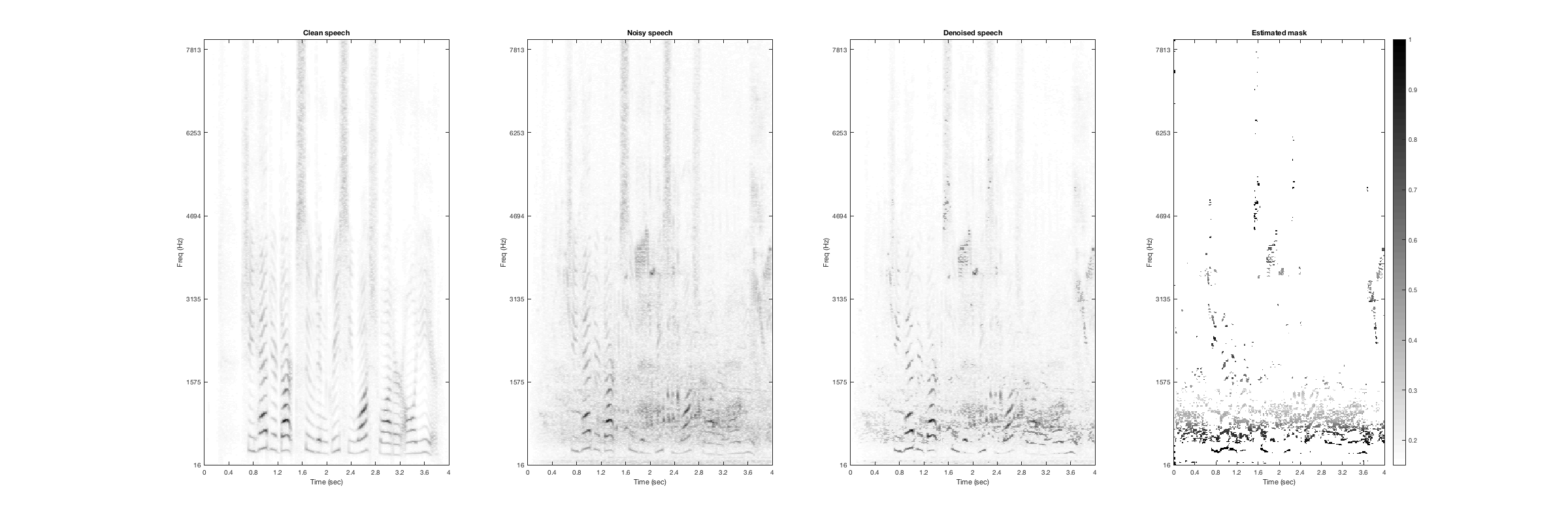
Machine guns
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 10.233):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
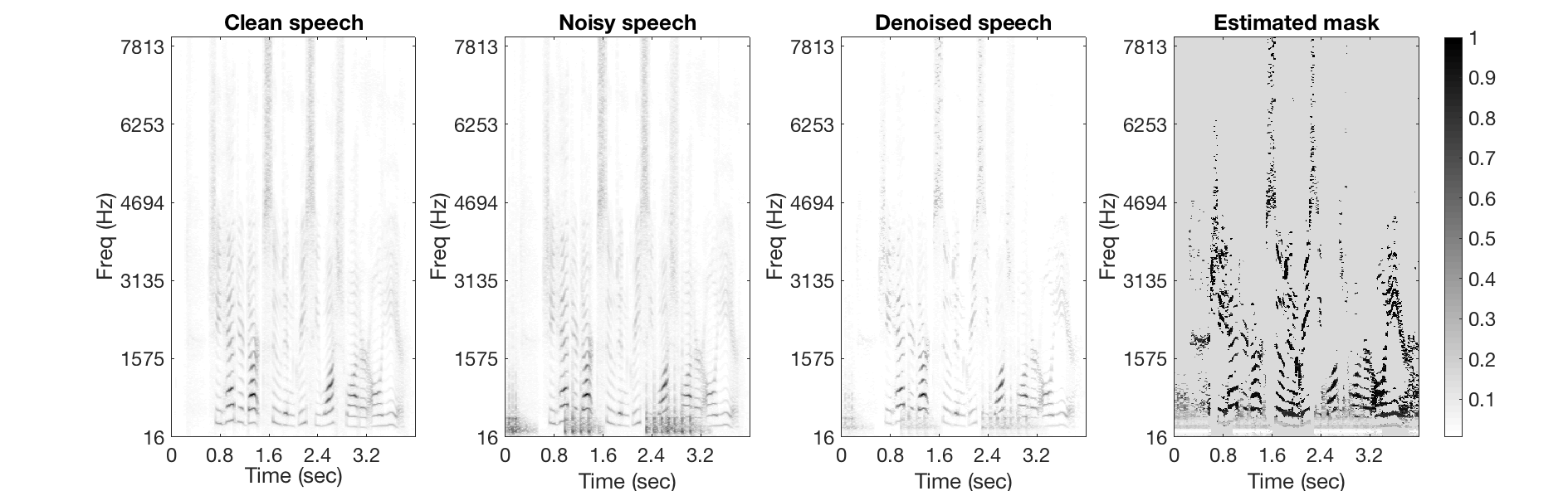
Motorcycles
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 8.6997):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):
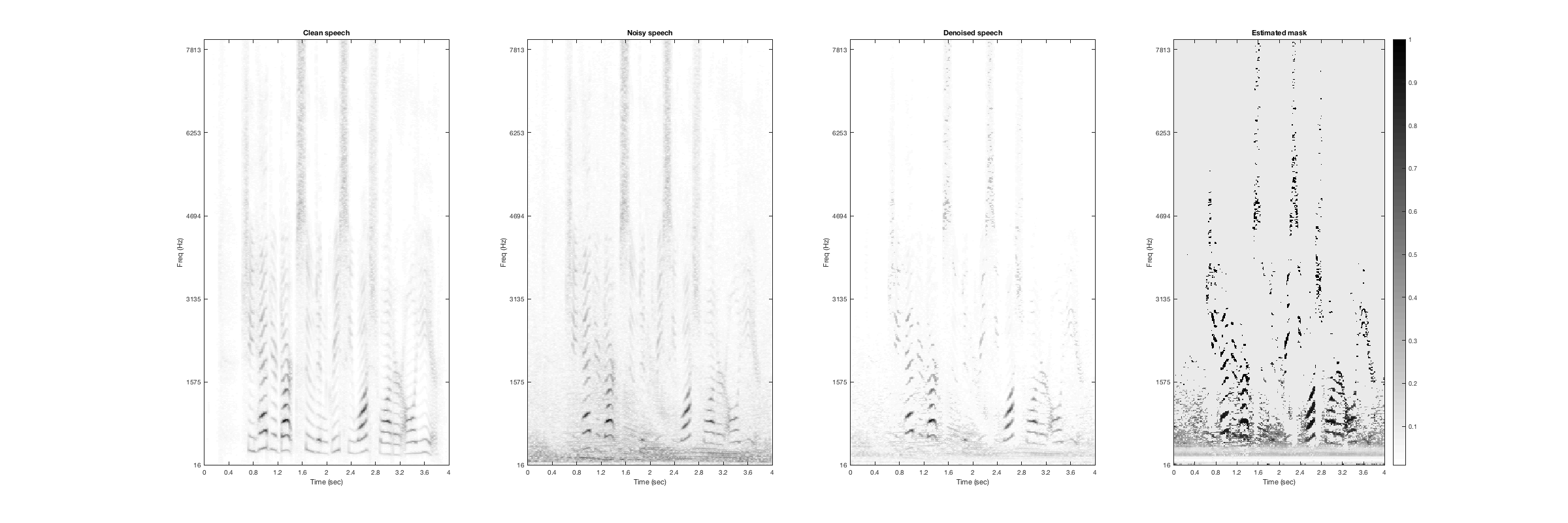
Ocean
Noisy Speech:
Denoised Speech (SDR = 6.468):
Magnitude Spectrogtam (From left to right: clean, noisy, denoised, mask):